Spaghetti Models for Tropical Cyclones: Spaghetti Models Beryl
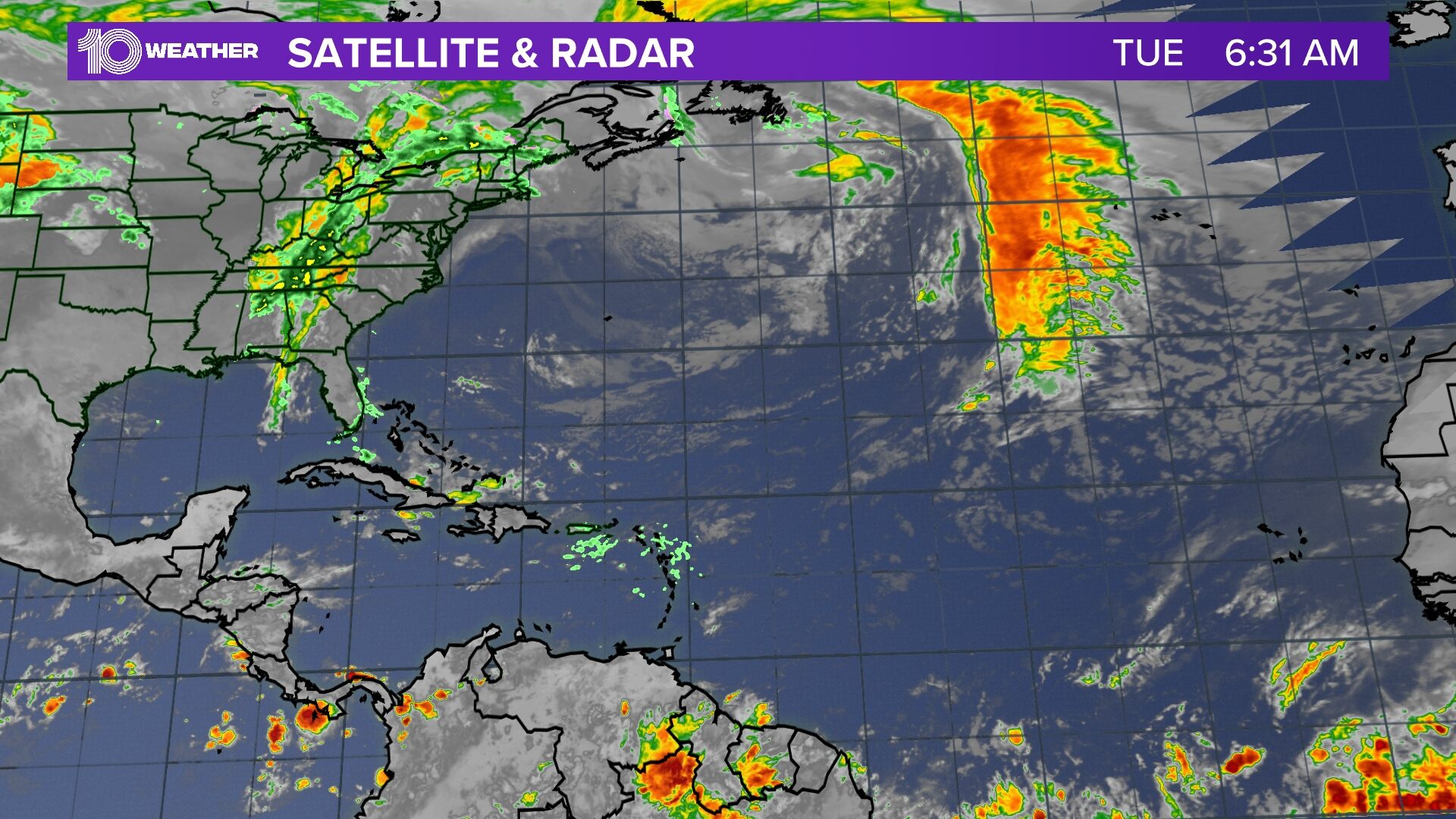
Spaghetti models beryl – Spaghetti models are a type of ensemble forecast model used to predict the path of tropical cyclones. They are created by running a computer model multiple times, each time with slightly different initial conditions. The resulting set of model runs is then displayed as a spaghetti-like plot, with each line representing a possible track of the tropical cyclone.
Spaghetti models are a useful tool for forecasters because they provide a range of possible outcomes, rather than a single deterministic forecast. This information can help forecasters to identify areas that are at risk of being impacted by the tropical cyclone, and to issue warnings accordingly.
Spaghetti models beryl ain’t no common pasta dish. It’s a whole lotta science that helps us understand the weather. And just like how puerto rico is a hub for culture, spaghetti models beryl is a hub for weather forecasting. It crunches data, makes predictions, and keeps us one step ahead of the storm.
So, next time you’re slurping on some spaghetti, remember the spaghetti models beryl that’s working hard behind the scenes to keep you safe.
Strengths and Limitations, Spaghetti models beryl
One of the strengths of spaghetti models is that they can provide a more accurate forecast than a single deterministic model. This is because the spaghetti model takes into account the uncertainty in the initial conditions, and produces a range of possible outcomes that reflect this uncertainty.
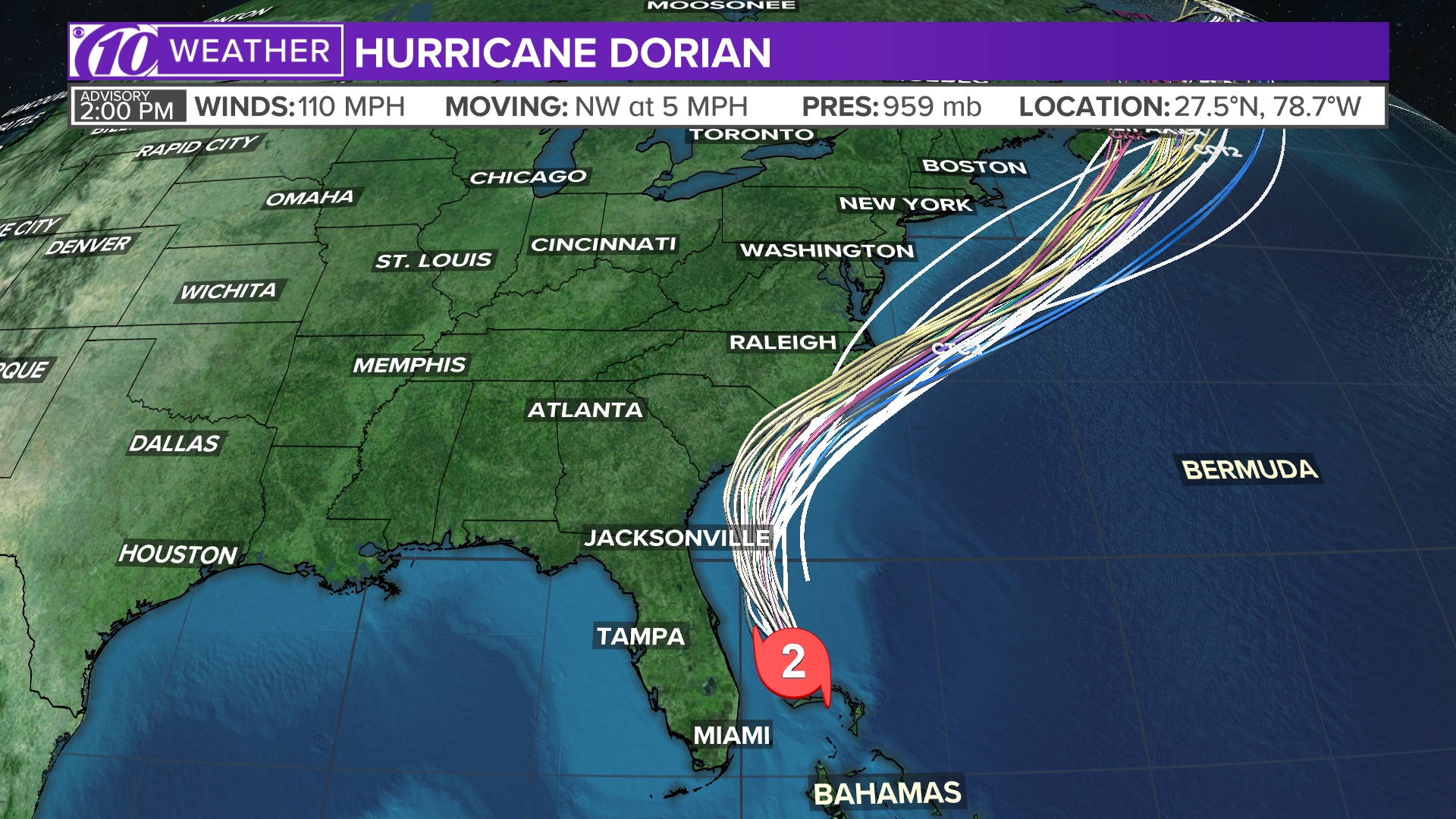
Spaghetti models beryl, named after a popular weather forecaster, are a type of computer model used to predict the path of tropical cyclones. These models use a spaghetti-like representation of possible cyclone tracks to show the uncertainty in the forecast.
Spaghetti models are an important tool for emergency managers and the public, as they can help to identify areas that may be at risk from a cyclone.
However, spaghetti models also have some limitations. One limitation is that they can be computationally expensive to run. This is because each model run requires a significant amount of computer time. Another limitation is that spaghetti models can be difficult to interpret. This is because the spaghetti-like plot can be difficult to read, and it can be difficult to identify the most likely track of the tropical cyclone.
Examples
Spaghetti models have been used to predict the paths of tropical cyclones for many years. One example of how spaghetti models have been used is in the forecasting of Hurricane Katrina in 2005. The spaghetti model for Hurricane Katrina showed a wide range of possible tracks, including one that would have taken the hurricane directly over New Orleans. This information helped forecasters to issue warnings for New Orleans, and to evacuate the city before the hurricane made landfall.
Case Study: Hurricane Beryl

Hurricane Beryl was a Category 4 hurricane that formed in the Atlantic Ocean in July 2018. The spaghetti models for Hurricane Beryl predicted a wide range of possible paths for the storm, with some models indicating that it would make landfall in the United States, while others predicted that it would remain out to sea.
In the end, Hurricane Beryl did not make landfall in the United States, but it did pass close to the coast of North Carolina, causing some damage. The spaghetti models were able to accurately predict the general path of the storm, but they were not able to pinpoint its exact landfall location.
Challenges and Successes
The spaghetti models for Hurricane Beryl were able to accurately predict the general path of the storm, but they were not able to pinpoint its exact landfall location. This is a common challenge with spaghetti models, as they are only able to provide a range of possible paths for a storm.
However, the spaghetti models for Hurricane Beryl were able to provide valuable information to forecasters, who used them to help make decisions about when and where to issue warnings and evacuations. The models also helped to keep the public informed about the potential risks from the storm.
Best Practices for Using Spaghetti Models
Spaghetti models provide valuable insights into the potential paths of tropical cyclones. However, it’s crucial to use them judiciously and in conjunction with other forecasting tools. Here are some best practices to enhance their effectiveness:
Interpreting Spaghetti Models
- Understand that spaghetti models represent an ensemble of possible tracks, not a single deterministic forecast.
- Consider the spread or “spaghetti” of the tracks to assess the uncertainty in the forecast.
- Pay attention to the “spaghetti soup” areas where the tracks converge, as these indicate higher predictability.
Considering Other Forecasting Tools
Spaghetti models should not be used in isolation. Integrate them with:
- Official forecasts from reputable agencies like the National Hurricane Center.
- Ensemble forecast models that provide probabilistic outlooks.
- Real-time observations, such as radar and satellite data.
Improving Preparedness
- Use spaghetti models to identify potential impact zones and develop evacuation plans.
- Monitor the models regularly to track changes in the forecast and adjust preparedness measures accordingly.
- Stay informed about the latest forecasts and advisories from official sources.